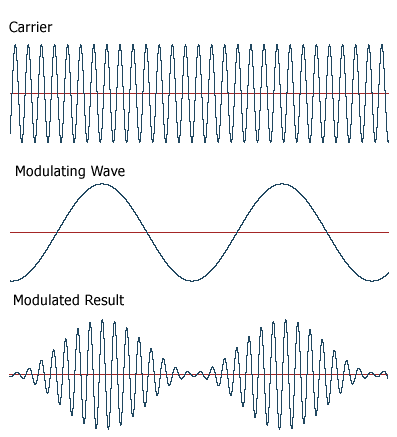
Modulation
It is the transmission of a signal by using it to vary a carrier wave, changing the carrier's amplitude, frequency or phase. Besides that, it is the process of conveying a message signal. Modulation is the process of converting digital signal to analog signal. Modem is the device that is used for the modulation process.
Demodulation
It is a process of retrieving data or message conveyed from the modulator. Besides that, it interprets and changes the signal delivered by the modulator. Demodulation process converts analog signal to digital signal. Modem, the same device used for the modulation process is also used in this process.
Bandwidth
TCP/IP

Short for transmission control protocol/internet protocol, it is the standard protocol or rules for the Internet. It allows different kinds of computers on different networks to communicate. Therefore, connecting them by a "universal" language. The essential features of TCP/IP is are identification and packetization. Identification is to identify sending and receiving devices whereas packetization reformats the information for transmission across the Internet. For identification, the internet uses IP address to deliver email and locate websites and the domain name server (DNS) converts the text-based adress to IP address. The function is the similar to a postal address. Packetization transmits information through interconnected networks. Before a message is sent, it is reformatted into packets and each packet is sent separately through the Internet. These packets are then reassemble into the correct order when received.
Node
Client
Server
Network Operating Systems
Network Administrator
It is a measurement of data that can be carried from one point to another in a given time period. Bandwidth is usually measured in bits (of data) per second (bps). For example, to transfer texts or documents, a slow bandwidth is used and to transfer audio or video files, a wider bandwidth is needed. There are three types of bandwidth which are voiceband (used for dial-up service), medium band (leased lines) and broadband (used for DSL and high capacity transmission).
TCP/IP

Short for transmission control protocol/internet protocol, it is the standard protocol or rules for the Internet. It allows different kinds of computers on different networks to communicate. Therefore, connecting them by a "universal" language. The essential features of TCP/IP is are identification and packetization. Identification is to identify sending and receiving devices whereas packetization reformats the information for transmission across the Internet. For identification, the internet uses IP address to deliver email and locate websites and the domain name server (DNS) converts the text-based adress to IP address. The function is the similar to a postal address. Packetization transmits information through interconnected networks. Before a message is sent, it is reformatted into packets and each packet is sent separately through the Internet. These packets are then reassemble into the correct order when received.
Node
It is a connection point for networks. It can be any device connected to a network. For example, a computer, printer, a data storage device or an active electronic device that is attached to a network. Besides that, it is capable of sending, receiving or forwarding information over a communications channel.
It is a node that requests and uses resources available from other nodes. Basically, a client is a user’s microcomputer. Besides that, a client is capable of obtaining information and applications from a server. Clients make "requests" through a network or networks, and receive "responses" from servers.
Server
It is a a node that shares resources with other nodes. Servers provide essential services across a network through the Internet. There are many servers and each of them are assigned to a specific task. Dedicated servers that are assigned to a specific tasks are web servers, print servers, and database servers.
Network Operating Systems
It is an operating system that has special functions for connecting computers and devices into a local-area network (LAN). NOS controls and coordinates activities of all computer and devices on the network. Such activities include electronic communication and the sharing of information and resources. Examples of networking operating systems are Novell Netware, Artisoft's LANtastic, Microsoft Windows Server, and Windows NT.
A computer specialist who manages a communications network in an organization. Responsibilities include implementing new networks, maintaining network operations efficiently and network security. Besides that, installing new hardware and applications, monitoring software upgrades, enforcing licensing agreements, developing a storage management program and providing for routine backups.